What is fulfilment?
The entire order processing of an order is an important process for companies that sell physical products.
Fulfilment in logistics refers to the assumption of the associated tasks and comprises a range of logistical processes.
Well-optimized logistics processes lead to fast order processing. This increases customer satisfaction, reduces costs, enables scalable growth and ultimately increases sales for companies.
Definition of: Fulfillment
The definition of the English term fulfilment ➚ (also “fulfillment”, “compliance”, “fulfilment”) means fulfillment, execution, order fulfillment, order processing, contract fulfillment and service from a single source.
However, the term is also used in English for a fulfilled and satisfied life. We refer here to the provision of logistics services.
What does e-fulfilment mean?
The term e-fulfillment refers to the fact that the entire order processing of buyers from the online store is handled exclusively for e-commerce retailers.
While fulfillment also involves order processing for regular dealers, wholesalers or retailers.
Understanding fulfillment in logistics
In logistics, fulfilment means providing the necessary services for the entire order processing process to fulfill an order placed by a customer or retailer.
In a nutshell, fulfilment comprises the following steps:
- Goods Receipt,
- Preparation of goods,
- Storage,
- Packing of the goods,
- Order acceptance,
- Picking of the goods,
- Packing,
- Shipping and
- Returns Management.
A company can handle the processing itself or outsource the tasks to an external partner.
Party Logistics
These logistics processes can be handled by a single company (all services from a single source) or outsourced by several companies.
The most common procedure on the market is to take over the entire transactions of 3 companies:
- 1 company for the procurement of goods and sales,
- 1 Fulfilment service provider for warehousing, picking, packing and shipping,
- and 1 company for delivery.
This constellation is referred to as 3 PL fulfillment.
A classic 2 PL fulfillment provider is Amazon by Fulfilment (FBA), for example. Retailers can outsource all tasks here. Offer their products on the marketplace, use storage space, pick & pack and delivery to the customer by Amazon Fulfillment.
However, Amazon places some demands on online retailers. If activity is too low and the LBI (inventory index) is too high, it may be more beneficial for retailers to use an external fulfilment provider for Amazon. This is then called the pre FBA service.
7 Core tasks in fulfilment
- Warehousing
- Order acceptance
- Assembling the goods
- Packing the goods
- Franking and labeling
- Shipping
- Returns
1. Warehousing
The first part of warehousing is goods receiving.
The goods are delivered by container, on pallets or in outer cartons. These can be single-variety or mixed. If mixed goods are delivered, the items or outer cartons are scanned and stored individually.
It is important that all goods are clearly labeled and can be stored quickly via a barcode in the goods management system.
What is the difference between a warehouse and a distribution warehouse?
In warehouse logistics, goods are temporarily stored in a large warehouse. The goods are delivered to the desired recipient when an order is called off. This can be a wholesaler, another fulfillment center or a provider of a marketplace platform.
Distribution warehouses are logistics centers where retailers’ goods are stored, picked, packed and from where customer orders are shipped directly to end customers. This offers the advantage of central processing.
Optimize inventory management
Inventory management of items in the merchandise management system is of great importance in warehouse logistics. This means that retailers must be able to keep track of stock levels, draw up an inventory and forecast demand to ensure that sufficient stock is available for retailers to meet the requirements of all customer orders.
The logistics service provider takes control of the stock of goods in the merchandise management system. If the picker removes a product from the warehouse, the stock is automatically reduced.
Using inventory management software automates many processes and adjusts inventory in the store or online dashboard.
This prevents stock shortages, reduces excess stock and improves the overall efficiency of warehouse work and goods management.
2. Acceptance of the order
In order to retrieve customer orders from the online store, ERP or merchandise management system (Wawi) to the warehouse, a connection must be established with the retailer’s system and the fulfilment provider via an API interface. The necessary data exchange process is bidirectional in both directions.
After the order is automatically retrieved, usually in real time, the order confirmation with tracking numbers and shipping notifications to the retailer are part of the shipping process.
Item master data maintenance
In order to be able to process orders quickly, it is important that the items are clearly labeled and the master data is maintained. The basic data includes the name of the item, SKU, EAN, weight, size, color and purchase price.
Retailers can provide the service provider with additional data when retrieving orders based on product factors and shipping preferences to optimize the process.
In addition to the transmission of the basic data (the so-called “original load”), product values such as attributes, serial numbers, Amazon FNSKU, TARIC code, hazard numbers, UN numbers, UPC, ISBN, barcodes and images can be transmitted, for example with JTL-Wawi.
By setting up shipping preferences, retailers can determine which shipping service provider and shipping method should be used for order processing for which products or destination country.
By automating the processes, retailers receive an overview of the individual steps of ongoing processes. This makes it possible to check whether customer orders are being fulfilled quickly and accurately. Some fulfillment service providers offer the service of displaying the processes in a portal or web-based dashboard.
3. Assembling the goods
Once the customer has placed the order, it is processed in the fulfillment center. Depending on the order, one or more of the items requested by the customer are put together (pick & pack), known as single-stage or multi-stage picking.
Nowadays, the “packangels” in the warehouse are either fully automated robots or warehouse specialists.
While robots offer the advantage of being able to perform many standardized tasks, picking and packing sensitive products by warehouse employees is still better.
In logistics, there are already “dark warehouses”. These work fully automatically 24/7 and naturally require no light because there are almost no people working in the warehouse.
In practice, hybrid models are often used. Here, automation helps warehouse employees (packangels) to carry out complex or heavy work steps more quickly with the help of machines.
Fulfilment service providers charge different prices for picking the goods. Some charge a flat rate for the entire process, while others charge for individual items such as incoming orders, the quantity of items and the SKUs. Returns processing is also charged differently. Prices vary from simply accepting the return to a visual and functional check.
4. Packing the goods
At the packing table, employees in the warehouse professionally pack the assembled items from the customer order in a suitable box. For this purpose, wet adhesive tapes, reinforced corrugated cardboard and filling material are used.
There are different packaging options depending on the product. For example, there is special packaging for bottles or posters.
The cardboard packaging can be made of environmentally friendly material and different thicknesses.
Some providers offer the customer service of gift-wrapping the items.
Either the retailer’s cardboard packaging or that of the logistics service provider can be used for packing.
Fulfillment on demand is also offered in some cases. In this case, personalized cards, inserts or flyers are printed and enclosed with the package.
Retailers must ensure that they are entered in the packaging register, even if they use an external logistics service provider. Since July 3, 2021, the legislator has stipulated that the distributor or manufacturer of the goods must register the shipping packaging and participate in the system.
When it comes to pick & pack, the provider’s team is an important factor in logistics. Well-rehearsed workflows for warehouse specialists are a decisive success factor.
5. Stamping, labeling and declaring consignments
Once the items have been securely and properly packed, the shipment must be sufficiently stamped, labeled and, in some cases, declared to customs.
Shipping labels are sometimes created directly by the retailer and transferred to the warehouse. They are usually created by the fulfilment service provider and applied to the shipment.
The belt size, weight, address, destination country and type of delivery must be taken into account for franking. There are also special regulations, such as shipping to islands or certain customs regulations that must be declared on the shipment, as well as shipping to Switzerland, the UK or Northern Ireland.
Certain products must be properly marked on the outside of the carton. This can be indications for batteries, dangerous goods, packages over 31.5 kg or easily breakable products in the shipment.
6. Shipping
Shipping with on-time delivery is a crucial component for customer satisfaction in e-commerce. The handling process and communication in fulfillment must run smoothly.
In many cases, customers expect fast shipping within 1-2 days. Delays or errors can lead to negative evaluations and lost sales precisely then.
Logistics companies often use transport companies such as DHL or DPD for shipping, which use their extensive experience to deliver goods to customers in Germany, throughout the EU and worldwide on a daily basis.
In the B2B area, the shipping service provider UPS is often used. This offers high reliability and quality in direct delivery of even large and delicate products.
Some retailers can also continue to use their own shipping account with the logistics service provider or they can use their own account. Each retailer receives their own billing number and the shipping prices depend on the order volume.
To optimize shipping and delivery, the fulfilment software should transmit the current status and tracking number to the online store or ERP dashboard. This allows customers to track the shipment precisely.
Sellers can also offer their customers various shipping options during the ordering process, such as express shipping, merchandise mail, bulky goods or international shipping.
Storage locations can also be defined by the customer. According to experience, this increases the regular delivery rate and avoids errors during delivery.
Some deliveries, such as bulky goods or pallets, can only be delivered by a forwarding agent. This option must also be stored in the retailer’s system and in the logistics provider’s merchandise management system.
Online retailers should communicate with customers and the service provider throughout the entire shipping process.
This allows information on tracking, any delays or problems to be provided quickly by the parcel service provider. Then the support can react in time and offer an individual solution.
To do this, the seller relies on receiving this data automatically from the shipping service provider or the warehouse.
If the delivery processes are set up optimally and the products are delivered reliably, customer expectations are met, satisfaction increases and returns are reduced.
7. Returns management
The average returns rate in e-commerce is 28%. So every third delivery comes back. The return must be accepted, unpacked, inspected, partially reconditioned or destroyed.
For sellers, this means enormous effort and costs. In addition to the product costs, there are the costs for shipping and returns.
Some of the returns can be resold as B-goods at a discount. Otherwise, the items must be disposed of properly, which in turn costs money.
These entire returns processing processes with customer support are also carried out by the fulfilment partner.
Other fulfillment services
In some cases, the fulfilment provider takes over additional services.
These include:
- Invoicing
- Dunning system
- Payment processing
- Cross Docking
- Marketplace pre Fulfillment
- After-Sales-Service
- On-Demand Product Fulfillment
Fulfilment costs
Fulfillment fees are charged based on the service provided. The effort can be charged per hour or per unit. A monthly basic fee is also often charged.
Roughly speaking, fulfillment costs can be divided into 4 areas:
- Incoming goods
- Storage
- Picking and packing
- Outgoing goods
Additional services, such as the packaging of items, customs declaration, enclosure of flyers, gift wrapping, processing of returns or refurbishment are charged additionally by agreement and with proof of the effort involved.
Costs may also be incurred for the storage of the goods. You should take this disadvantage into account when selecting a provider.
What are the biggest cost drivers?
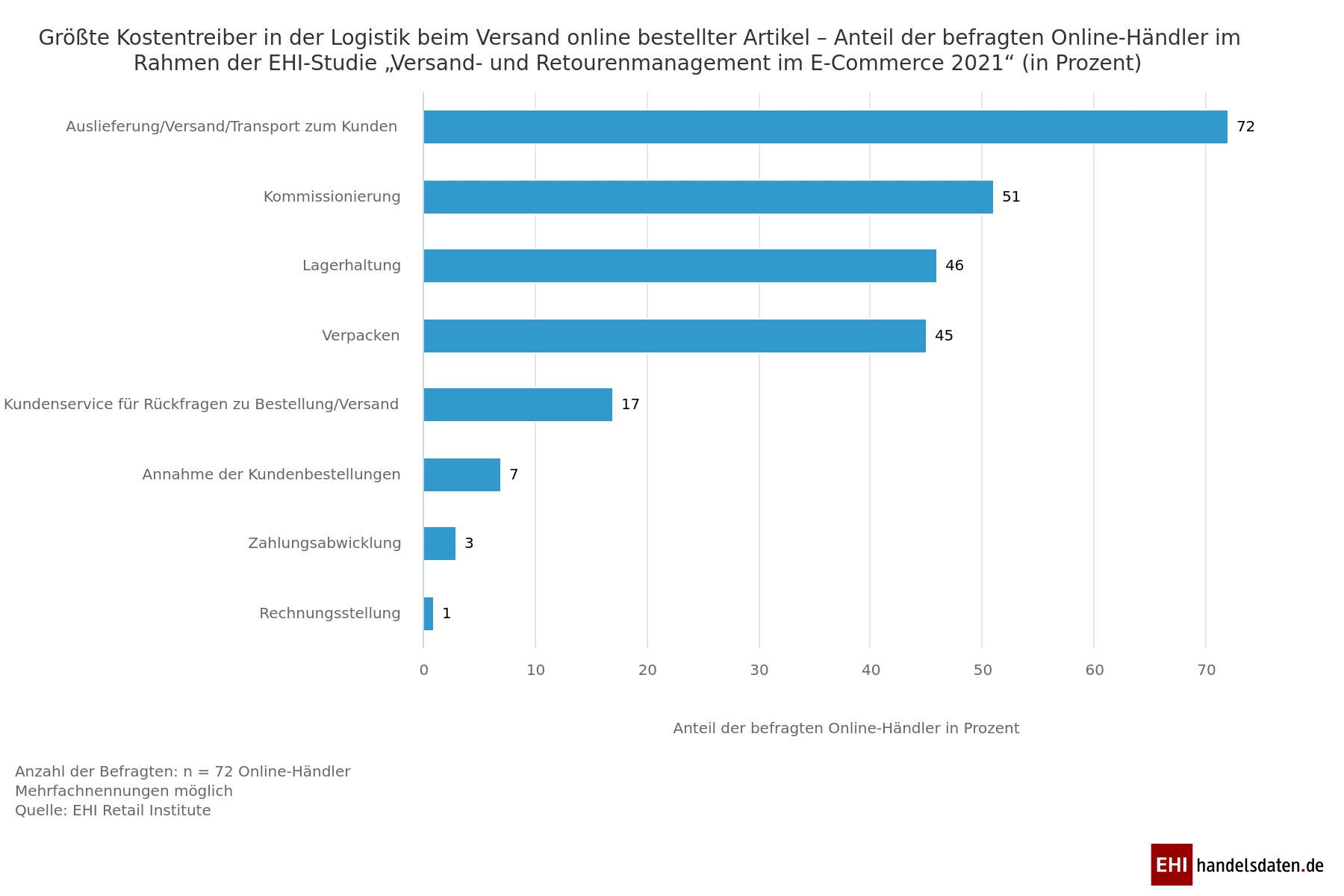
Source: © EHI-Studie ➚ „Warehousing, transport and returns processing in e-commerce 2021“
Sellers: in e-commerce, as in bricks-and-mortar retail, they have to bear some costs. Retailers must therefore charge prices for their products that offer a sufficient margin.
With high competition and low specialization, there is usually high price pressure on the market, especially in e-commerce. This is an opportunity to reduce costs by bundling and optimizing tasks.
Retailers can use clever mixed costing to offer customers attractive deals and highlight them, especially on special offer days. The additional logistical effort can be absorbed by an external logistics service provider by deploying its employees as required.
Fulfilment goal
By outsourcing to a fulfillment operator such as Fiege Now, Orange Connex, Subke, Rhiem, lufapak, DHL or DPD, around 80% of entrepreneurs hope to gain a competitive edge, use external resources to fulfill time-consuming tasks and make their work significantly easier.
Logistics providers should ensure a scalable, cost- and process-optimized service for online retailers with a reduced error rate. They are an important component for efficient storage, management and control of the flow of goods and information.
Practical advantages of using this logistics solution:
- Taking over the inventory management of the articles including stocktaking,
- Taking over the entire order processing,
- Retailers can concentrate more on their core business,
- Shortening order processing,
- Increase customer service,
- Take-back and possible professional disposal of the products,
- Increase in bearing frequency,
- Leverage specialized logistics and expertise (pre FBA),
- Sending bulk mailings,
- Reduction of inventories.
70% of online stores already use a fulfilment service. However, only around 40% of companies with an annual turnover of less than €5 million do so. This is due to the fact that smaller companies start with in-house fulfilment, while companies with strong growth prefer to use an external provider.
Competitive advantages through fulfillment
In online business, there is a certain selection of logistics providers available, which differ in terms of target group, tasks and fees.
If a logistics company supports a company, it has the opportunity to utilize complex services and achieve its own competitive advantages through cooperation.
Retailers and online retailers say they want to improve the following services by outsourcing tasks to a third-party provider:
- Optimization of the order status for customers,
- Improved returns processing with inventory reporting and photo creation,
- more sustainability in packaging and shipping,
- Reprocessing of the products,
- Planning and controlling the flow of goods, information and money along the entire supply chain,
- Flexibility in the use of storage space,
- Reduce the risk of incorrect picking and delivery,
- Absorbing the higher workload on action days,
- Locations of storage with good infrastructure to the end customer,
- Customer care,
- Transmission of the electronic signature upon delivery of the shipment,
- Collection service of the goods,
- Payment processing by invoice.
When is fulfilment worthwhile?
Fulfilment is suitable for companies and organizations that want to benefit from efficient, reliable and professional handling of storage, shipping and returns of their products. Here is a summary of who fulfilment is particularly suitable for:
- E-commerce companies: Fulfilment is an ideal solution for e-commerce companies and brands that need to process a large number of online orders. It allows them to outsource storage and shipping so they can focus on marketing and growing their business.
- Small businesses: Small businesses that have limited storage capacity or do not want to specialize in logistics tasks can benefit from fulfilment services. It enables them to keep their operating costs low and still offer professional shipping.
- Startups: Startups with limited resources can use fulfilment to reduce their operating costs while having a scalable solution for shipping. This facilitates growth and expansion.
- Companies with seasonal business: Companies that have strongly fluctuating seasonal sales figures can use fulfilment to react flexibly to changes in demand. You don’t have to worry about adjusting your storage capacities.
- Companies that want to concentrate more on their core business: Fulfilment allows companies to focus more on their core business while outsourcing logistics tasks to specialists. This leads to greater efficiency and productivity.
- Companies that need fast and reliable shipping: Fulfilment partners can often ship faster and more reliably, which increases customer satisfaction and makes companies more competitive.
- Companies looking to expand internationally: Fulfilment can be helpful for companies looking to expand internationally, as it makes it easier to process orders in different countries and regions.
Overall, fulfillment is a versatile solution that provides important support for companies of all sizes and industries to optimize their logistics processes. At the same time, time and resources are freed up for the main business.
+ Pros:
Outsourcing tasks: relieving the company of time-consuming tasks.
More time for core business: focus on strategic and important tasks.
External storage capacity: Access to additional storage capacity without own investment.
High number of orders can be processed: scalability and flexibility in order processing.
Professional packaging and shipping: ensuring high-quality and reliable delivery to customers.
Flexible access to employees: If necessary, a larger team can be deployed to handle the tasks.
– Cons:
Dependent on the third-party provider: Risk of dependency and trustworthiness of the service provider.
Bound by long contract terms: Restriction of flexibility with contract commitment.
Difficult quality control: the challenge of ensuring quality standards.
Increased communication necessary: Need for close cooperation and constant coordination.
Price adjustment: Possible price increases due to external service provision.
Extensive contractual obligations: A key point in fulfilment is the service contract. This should be carefully examined and negotiated if necessary.
Please note that this is a general overview and there may be individual advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific situation and needs of the company.
As a next step, it is best to obtain a comparison with several offers, arrange a visit to the warehouse and a consultation appointment with the future contact person.
Results of the fulfillment survey
The question was: “What is particularly important to you in fulfillment?“
As a percentage of participants surveyed. Number of respondents: 2023 n=95 Source: subke.com
FAQ - Fulfilment
- What is the difference between fulfilment and eFulfilment?
While order processing in fulfilment includes all retailers, eFulfilment is aimed exclusively at online retailers with order processing for their end customers in e-commerce.
Fulfilment includes the service for B2B and B2C businesses. Instead, companies in eFulfilment mostly cover B2C and D2C businesses. - What is Party Logistics?
Another term that describes how many parties are involved in the logistics process.
For example, an online retailer can take on the fulfilment tasks itself.
The term ‘third-party logistics’ is used when a professional logistics service provider takes on the tasks. In general, a distinction is made between 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL and 5PL services.
- What is order picking?
Picking is the process of assembling goods or products from a warehouse to fulfil orders from customers or other departments. This can be manual or automated and often includes packing and despatching the orders.
- What does customisation mean?
Packaging refers to the process of assembling and packing products to make them ready for sale or dispatch. This can include, for example, assembling individual parts into a finished product, labelling or packaging in boxes or film.
- How do you frank a parcel?
To frank a parcel correctly, you need to know the weight and size (the girth) of the parcel. You can then either buy a franking label online and print it out or use a franking machine. Alternatively, you can also go to the post office and have the parcel franked there. Make sure that you choose the correct shipping method and write the recipient's address clearly on the parcel.
- What is labelling?
Labelling refers to the application of labels to products or packaging in order to communicate information such as ingredients, origin, shelf life or warnings. It is used to label and differentiate products and is required by law in many industries.
- What does it mean to declare a parcel?
The sender officially declares the contents of the parcel by completing a shipping label or a shipping declaration.
The declaration includes the name of the sender and the recipient, the exact address, the weight and dimensions of the parcel and a detailed description of the items contained.
It is important for the customs authorities if the parcel crosses international borders and for the insurance company in the event of liability for loss, damage or theft. - What does pre fulfilment mean?
The ‘pre-fulfilment’ service is often used by online retailers who sell their goods on marketplaces such as eBay, Amazon or Zalando, but who use an external fulfilment service provider rather than the marketplace provider for warehousing and, in some cases, order processing. The best known of these is the pre FBA service (Fulfilment by Amazon).
- What is a fulfilment partner?
A fulfilment partner handles storage, shipping and returns for companies. They offer:
- Storage: Storage space in their own or third-party warehouses.
- Shipping: Delivery by parcel, courier or postal service.
- Returns: Processing of customer returns, costs depending on agreement.
Advantages for companies:
- Time saving: Focus on core business.
- Cost savings: Less expensive storage and shipping.
- Improved customer satisfaction thanks to fast dispatch.
Relevant for companies of all sizes, especially:
- Small or stockless businesses.
- Companies focussing on fast, reliable shipping.
- What is DHL Fulfilment?
DHL Fulfilment is a service offered by DHL eCommerce Solutions, a division of DHL, a leading global logistics company.
DHL Fulfillment offers companies solutions for the storage, shipping and fulfilment of e-commerce orders and fulfilment services.
Here are some examples of companies that use DHL Fulfilment:
- E-commerce companies: DHL Fulfillment is a popular choice for e-commerce businesses looking to offer fast and reliable shipping.
- Wholesalers: DHL Fulfillment is also a popular choice for wholesalers who want to ship their products to customers across Europe.
- Manufacturers: DHL Fulfilment can also be used by manufacturers who want to ship their products to retailers or end customers.

